



On January 29th, Ride Illinois was honored to issue a statement related to e-bikes, e-scooters, and micromobility at a press conference convened by Illinois Secretary of State. Our statement emphasized the need for common sense legislation that aims to integrate new mobility modes into Illinois communities while retaining a clear focus on public safety.
At the press conference, Secretary Giannoulias announced a new multi-pronged campaign – Ride Safe, Ride Smart, Ride Ready – that combines public education, updated driver training and a push for modernized safety laws to keep pace with the fast-evolving micromobility industry.
Ride Illinois will continue to collaborate with Secretary of State Giannoulias, State Senator Ram Villivalam, State Representative Barbara Hernandez, the Illinois High School and College Drivers Ed Association, Illinois Association of Chiefs of Police, and additional partners to develop balanced legislation that embraces new mobility modes while retaining a strong focus on public safety.

Ride Illinois hosted a webinar, in partnership with the Active Transportation Alliance, in August 2025. The webinar aimed to educate elected officials, municipal staff, law enforcement, planners, advocates, and the public on the important distinction between legal e-bikes and e-motos.
The informative discussion touched on topics such as micromobility, the legal classes of e-bikes, the rise of e-motos, concerns raised by advocacy organizations, and the need to focus on long-term solutions with to safely integrate new mobility modes into Illinois communities.
The recording and slides from the presentation are available below. Contact info@rideillinois.org with questions about this matter.
Ride Illinois hosted a timely and informative webinar in December 2025. The goal of the webinar is to educate the public about the differences between e-bikes and e-motos, key safety considerations, and the why the patchwork of municipal ordinances is not an effective long-term solution. We also discussed the need for common sense legislation at the state level – a key priority for Ride Illinois during the 2026 legislative session.
The recording and slides from the presentation are available below. Contact info@rideillinois.org for more information.
This guidance encourages municipalities to embrace new mobility modes while retaining a focus on public safety. Municipalities that thoughtfully integrate new mobility modes are places where people – especially younger people – prefer to live, work, and play.
Ride Illinois is a nonprofit organization with a mission to make Illinois better through biking. Ride Illinois strives to make it safer, easier, and more practical for adults and children to move about their communities outside of motor vehicles. Bicycles remain at the core of Ride Illinois’ mission. New mobility modes (e-bikes, e-motos, e-scooters, and micromobility devices) are increasingly included in discussions at the local and state level. As a result, Ride Illinois has learned quite a bit about this emerging technology.
In recent years, e-bikes, e-motos, e-scooters, and other micromobility devices have grown in popularity. They provide inexpensive, practical mobility alternatives to motor vehicles. These devices are commonly used by those unable to drive or afford a motor vehicle. They also allow some people to live car-free or car-lite, thereby reducing transportation expenses – a reason for elected officials to embrace these new modes.
E-bikes, e-scooters, and micromobility devices are popular as they offer an inexpensive, environmentally-friendly, enjoyable mode of travel for recreation, transportation, and everyday trips. Ride Illinois recognizes that the industry has been moving faster than common sense regulations that ensure safety of riders and those they encounter. This guidance offers a practical approach to municipalities as they integrate new mobility modes into their communities.
Ride Illinois is opposed to outright bans on low-speed e-bikes, low-speed e-scooters, and micromobility devices. Bans often result in more trips by motor vehicle – the true cause of the vast majority of serious injuries and fatalities on Illinois’ roads. Over 99% of U.S. roadway fatalities are caused by motor vehicles. A strict crackdown on e-bikes, e-scooters, and micromobility devices is misdirected and deflects attention away from the real issue.
Ride Illinois encourages municipalities to integrate low-speed e-bikes, low-speed e-scooters, and micromobility devices into their transportation network and infrastructure. Given the wide-ranging implications, robust discussion with and intentional outreach to those who will be most impacted are essential prior to adoption of a local ordinance. An ordinance that impacts and/or restricts community mobility must not be developed nor voted on by local elected officials without providing the public with sufficient opportunity to express their opinions on the issue.
With few exceptions, the public doesn’t understand what is and is not a legal low speed e-bike. The term “e-bike” is being used to unfairly punish or restrict the use of legal e-bikes by Illinois residents – often by local elected officials. Some retailers and manufacturers are also culpable because they are marketing and selling devices as “e-bikes” that are not legal e-bikes per Illinois law.
Ride Illinois’ goal is to eliminate this confusion – and slow or stop the adoption of local ordinances – by clearly distinguishing between e-bikes and e-motos in the Illinois Vehicle Code. Laws recently passed in California, Colorado, Minnesota, and Utah could be a model for similar legislation in Illinois.
The State of Illinois approved three classes of low-power electric bikes in the Vehicle Code (625 ILCS 5/1-140.10) on January 1, 2018. Additional regulations regarding e-bikes can be found in (625 ILCS 5/11-1517). Illinois’ statute aligns with guidance developed by People for Bikes that has been adopted by 48 of 50 states.
Two- or three-wheeled vehicles with fully operable pedals and an electric motor of less than 750 watts are considered low-speed e-bikes in Illinois. Legal low speed e-bikes are only sold in adult sizes. The three legal, recognized classes of low-speed e-bikes are:
Low-speed e-scooters are devices weighing less than 100 pounds, with 2 or 3 wheels, handlebars, and a floorboard that can be stood upon while riding, that is solely powered by an electric motor and human power, and whose maximum speed, with or without human propulsion, is no more than 10 miles per hour. Per Illinois law, one must be 18 years of age or older to operate an e-scooter.
Micromobility devices include a broad range of lightweight, low-speed travel modes that serve as personal mobility and have a top assisted speed of 20 mph.
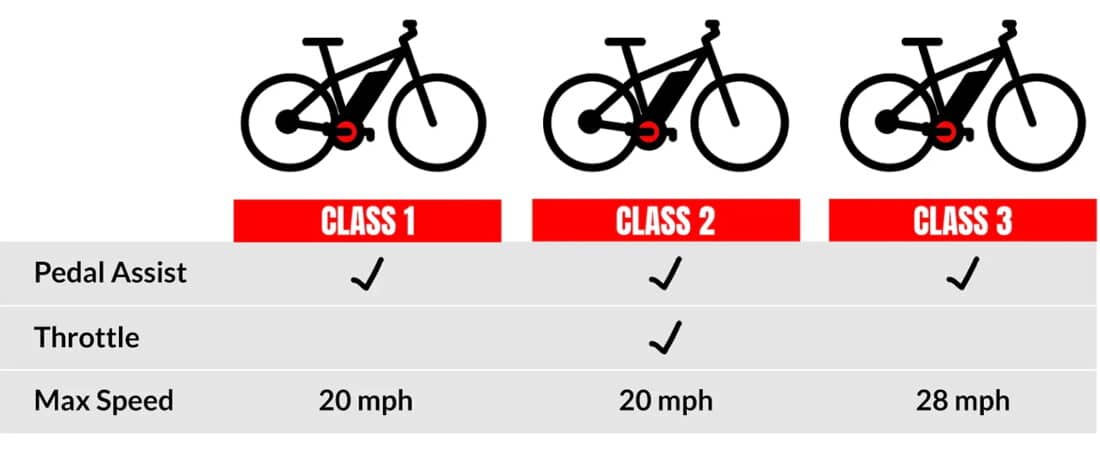
Ride Illinois supports People for Bikes’ three class system and their model legislation that was specifically designed to facilitate the regulation of low-speed electric bicycles that closely resemble human-powered bicycles in their equipment, handling characteristics, size, and speed.
Devices with an electric motor greater than 750 watts are not e-bikes. Any type of device with an electric motor beyond a Class 1, 2, or 3 electric bicycle is not a legal e-bike and should not be advertised, sold, offered for sale, or labeled as an e-bike. These devices are commonly referred to as e-motos (aka Out-of-Class Electric Vehicles (OCEVs)).
When used by adults, e-motos are only allowed in travel lanes intended for automobiles – not on trails of infrastructure intended for bicycles, scooters, personal mobility devices (such as motorized wheelchairs), or other legal modes.
Many devices that are marketed to children and teens fall into the e-moto category. These devices should only be used by children and teens on personal property – not on sidewalks, trails, bike infrastructure, or roads.

E-motos should be the focus of municipal ordinances as they are not legally defined in the Illinois Vehicle Code. E-motos typically:
Ride Illinois will be advocating for legislation to legally define e-motos in the Illinois Vehicle Code in the 2026 legislative session. Including a definition in the Illinois Vehicle Code will allow municipalities and local units of government to restrict the use of e-motos. This will also differentiate between e-bikes and e-motos there by alleviating some of the confusion caused by municipalities that were quick to introduce ordinances that restricted the use of legal e-bikes.
Once the definition of e-motos is added to the Illinois Vehicle Code, it would be prudent and wise for municipalities to revisit and revise ordinances to focus solely on e-motos. It’s likely legislation won’t be signed into law any sooner than summer of 2026.
Ride Illinois developed this guidance to reasonably address the concerns of elected officials, business owners, and residents pertaining to human-powered bicycles, e-bikes, e-scooters, and micromobility devices. It’s critical that, when developing a common sense ordinance, municipal staff discuss proposals with adjacent municipalities. This collaboration will result in consistency when individuals travel between communities. Ride Illinois recommends that municipal ordinances contain the following common sense elements:
* Unless restricted by the local ordinance, such as the City of Chicago.
The chart below offers a rational approach for elected officials, staff, business owners, and residents when developing a municipal ordinance.
The City of Rolling Meadows requested assistance from Ride Illinois to develop their municipal ordinance related to e-bikes and e-motos. It serves as a model for other municipalities feeling pressure to act in lieu of a state-level solution. The Rolling Meadows ordinance is available below.
E-bikes, e-scooters, and micromobility devices offer individuals who cannot drive or choose to not drive a reliable, inexpensive mobility option. Age, disability, personal choice, and lack of other transportation options are common reasons for using such devices. Also, these devices are frequently used by lower income individuals. Municipal ordinances must not be overly restrictive toward these individuals.
When developing a municipal ordinance, Ride Illinois strongly encourages decision makers to consider the impact on the following:
Municipal ordinances should include these reasonable elements to offer clarity to residents, visitors, and those who work within the community:
On 7/16/25, Ride Illinois spoke with Fox 32 Chicago about e-bikes and e-motos (aka OCEVs) in an effort to educate the public on the difference and push back on overly-restrictive municipal ordinances.
On 7/23/25, the Daily Herald published an article about the flurry of e-ordinances. Ride Illinois shared insights and recommendations for municipalities, while noting the benefits of new mobility modes.
On 7/24/25, Ride Illinois spoke with WBEZ’s Sasha-Ann Simons on Reset about the patchwork of rules and regulations that is leaving many potential riders confused on what they can and can’t do.
On 8/13/25, Ride Illinois contributed to an article in Axios Chicago about municipalities across the state responding to residents’ complaints about “mini motorcycles” and confusion about the difference between e-bikes and e-motos that has led some towns to restrict e-bike use.
On 9/22/25, Ride Illinois served as a panelist for the Summit on E-Bike/E-Scooter/E-Moto Ordinances hosted by the Northwest Municipal Conference. The Daily Herald summarized the panel discussion which focused on e-motos and the need for a state-level solution.
Click a graphic to download a high-resolution JPG.
Questions and comments related to this guidance can be sent to info@rideillinois.org. Also, Ride Illinois can be a resource for municipalities and local units of government seeking to develop a common sense approach to integrating and embracing new mobility modes.
Updated on February 1, 2026